- Home
- Services
Therapeutic plasmapheresis
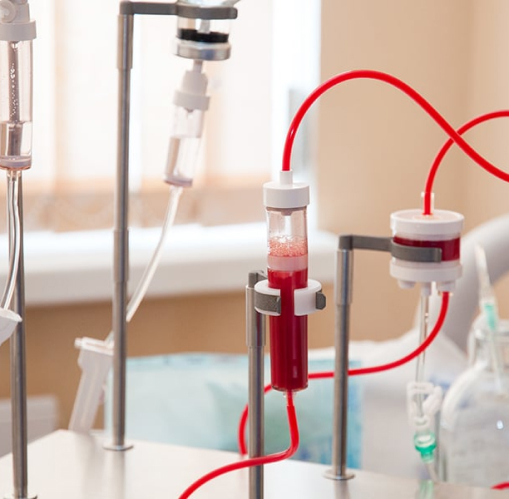
Plasmapheresis is a modern, safe, painless and atraumatic method of blood purification.
Plasmapheresis is the separation of blood by the subsequent removal of a liquid fraction - plasma with accumulated slags, the return of cellular elements and the compensation of the volume obtained by plasma substitutes. It is included in the complex of treatment of diseases caused by impaired immunity, metabolism, intoxication in the case of ineffectiveness of generally accepted therapy.
Due to a violation of blood circulation, an increase in the concentration of toxins (toxins), antibodies and immune complexes in the blood, there is a natural "cleansing" and "blockade" of the protective systems: liver, kidneys, lungs, immune system. Toxic substances enter the lymphatic system, blood flow and circulate in large quantities in the blood (plasma).
Then they accumulate in the tissues, causing damage to organs. Plasmapheresis allows you to stop this process. Slags are first removed from the blood, and then from the tissues (drying effect). When redeeming the resulting plasma, blood dilution is achieved. Stagnation in the capillaries (small vessels) decreases, the flow of fluid from the tissues increases, which helps to improve blood circulation and tissue respiration in all organs.
The therapeutic effect of plasmapheresis includes immunostimulating, anti-inflammatory, and detoxifying effects due to:
- Elimination of circulating immune complexes, reduction of the concentration of antigens, antibodies;
- Removal of microbes, toxins, and end products of metabolism (slags) with plasma;
- Elimination of inflammatory factors-prostaglandins, thromboxans, lymphokins;
- Removal of procoagulants, cryoglobulins – substances that increase blood clotting;
- Restoring the sensitivity of cellular receptors to hormones, drugs - reducing the dose of drugs taken to achieve the desired effect;
- Normalization of blood microcirculation and rheology and restoration of impaired metabolism.
Plasmapheresis in our blood center < / span> is performed by two main methods:
1.discrete (manual) plasmapheresis is performed using a centrifuge and sterile disposable hemocontainers with preservatives. Blood is taken, the containers are centrifuged, then the plasma is removed and the blood cells are returned to the patient. In addition, saline solutions are poured, which compensate for the volume of the resulting plasma. In just one session of plasmapheresis, 300-600 ml of plasma is taken. This is the most affordable method, the duration of 1 session is 2-2.5 hours.
2.automatic (hardware) method is based on the separation of a continuous flow of blood taken in the separator of the Haemonetics PCS-2 (USA) apparatus, combined with automatic supply of anticoagulant, automatic plasma sampling and return of cells to the venous canal. Hardware plasmapheresis is most suitable for the patient and has its advantages:
small volume of replenishment of the system for blood
continuous cycle of blood collection, division, and cell return
low blood cell damage
ease of use, significant speed.
the duration of the session is 60-90 Min, the volume of extracted plasma is 600-1000 ML.
both methods are performed using a single-needle method (puncture of one peripheral vein) using only single-use Flow Systems.
the effect of plasmapheresis is manifested after the first session. The concentration of pathological products is significantly reduced, but after a few hours their content in the blood approaches the initial level. This indicates that substances located in the extracellular interstitial space or cells have entered the root canal. Subsequent sessions of plasmapheresis contribute to the destruction of these substances, which leads to a complete restoration of the entire internal environment, given that most of the harmful products are located outside the vascular space. For a stable positive effect,1-1.5 sessions are required, removing 3-6 volumes of circulating plasma from the total volume. The resulting plasma is effectively compensated by saline solutions.
thus, the inclusion of plasmapheresis in the complex of therapeutic measures contributes to a more favorable course of diseases that are particularly difficult to treat with medication, significantly improving the condition of patients and reducing their drug load.
Presentation
- Allergic and autoimmune diseases: bronchial asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, dermatomyositis, autoimmune thyrioiditis (Hashimoto's goiter), pollinosis, chickenpox, otitis media, bacterial endocarditis, glomerulonephritis and others. Allergic and autoimmune diseases: bronchial asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, dermatomyositis, autoimmune thyrioiditis (Hashimoto's scarlet fever), pollinosis, angioedema, acute urticaria, bacterial endocarditis, glomerulonephritis and others.
- Skin diseases: eczema, psoriasis, neurodermatitis, atopic dermatitis, furunculosis, acne.
- Neurological diseases: myasthenia gravis, including myasthenia gravis crises are attacks of muscle weakness, multiple sclerosis at the initial stage, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, hyena-Barre syndrome (demyelinating inflammatory polyneuropathy), especially acute, in the initial stage, chronic fatigue syndrome.
- cardiovascular diseases: coronary heart disease, hypertension diseases of the foot, atherosclerosis of the vessels of the brain, high cholesterol (including familial hypercholesterolemia), high blood viscosity syndrome, vascular diseases (obliterating endarteritis, thromboangiitis, nodular arteritis, hemorrhagic vasculitis).
- liver diseases: toxic hepatitis, hepatosis, cirrhosis of the liver, infectious not jaundice, Gilbert's disease.
- metabolic diseases: diabetes, gout, porphyria, Wilson's disease, hemochromatosis.
- Obstetric and gynecological diseases: sexually transmitted chronic infections (chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, etc.), chronic inflammatory diseases of the uterine appendages, infertility, inability to tolerate pregnancy, toxicosis (gestosis) of pregnant women, hereditary thrombophilia, BFS syndrome, autosinsification of HCG, prevention of RH-contradictory pregnancy, climacteric syndrome.
- urological diseases: chronic prostatitis, chronic pyelonephritis, chronic renal failure, sexual disorders in men.
- blood diseases: thrombocytopenic purpura, cryoglobulinemia, myeloma disease, macroglobulinemia Valdenstrema, autoimmune hemolytic anemia.
- toxicological conditions: various poisonings, including narcotic drugs and elimination of toxic manifestations in alcohol poisoning.
CONTRAINDICATION
- bleeding (ulcers, tumors of the gastrointestinal tract, lungs, genitourinary system, etc.).
- acute stage of infectious and purulent inflammatory processes.
- hyperthermia.
- arterial hypotension, shock (AD < 90 MMR).
- exhaustion, total blood protein < 55 g/l
- anemia (NB& < 90g/l)



